The contains() method of Java HashSet class is used to check if this HashSet contains the specified element or not. It returns true if element is found otherwise, returns false.
- Hashset Sample Program Java download free, software 2014
- Java Hashset Add
- Hashset Sample Program Java Download free. software downloads
Java Barcode is a High Quality Java barcode generator to be used in J2EE, J2SE and Java Reporting environment. Free tutorial and trial download.
Syntax
- In order to create a hash set, we must import the java.util.HashSet package first. Once we import the package, here is how we can create hash sets in Java. // HashSet with 8 capacity and 0.75 load factor HashSet numbers = new HashSet(8, 0.75); Here, we have created a hash set named numbers. Notice, the part new HashSet(8, 0.75).
- HashSet class is one of the collection class in java. HashSet class extends AbstractSet and implements the Set interface. HashSet class is used to create a collection that uses a hash table for storage. Hash table stores the information using a mechanishm called hashing.
Following is the declaration of contains() method:
Parameter
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| o | It is the element whose presence in this set is to be tested. | Required |
Returns
The contains() method returns true if this set contains the specified element.
Exceptions
NA
Compatibility Version
Java 1.2 and above
Example 1
Test it NowOutput:
Example 2
Test it NowOutput:
Example 3
Test it NowOutput:
Next TopicHashSet isEmpty() Method
We are sharing the 10 most frequently asked java developer interview questions on HashSet . These questions fully covered the technical questions which can be asked on HashSet .Apart from the below questions interviewer may ask you to write code on HashSet object examples , iterations on HashSet object .We try to cover important Java developer interview questions which are frequently asked by the Big companies to the candidate on HashSet .
Q1. How Hashset works internally in Java or how HashSet works in java?
This question is asked by the reputed firms especially Goldman Sachs , J P Morgan . You can find the answer here Internal implementation of HashSet or How hashset ensures uniqueness in Java
Q2. What copy technique internally used by HashSet clone() method ?
There are two copy techniques in every object oriented programming lanuage , deep copy and shallow copy.
To create a clone or copy of the Set object, HashSet internally uses shallow copy in clone() method , the elements themselves are not cloned . In other words , a shallow copy is made by copying the reference of the object.
Q3 Why HashSet does not have get(Object o) method ?
Most of the people get puzzled by hearing this question . This question tests the deep understanding of the HashSet class .This question helps the interviewer to know whether candidate has the idea about contains() method in HashSet class or not .So let jump to the answer
get(Object o) is useful when we have one information linked to other information just like key value pair found in HashMap .So using get() method on one information we can get the second information or vice-versa.
Unlike HashMap , HashSet is all about having unique values or unique objects . There is no concept of keys in HashSet .
The only information we can derive from the HashSet object is whether the element is present in the HashSet Object or not . If the element is not present in the HashSet then add it otherwise return true leaving HashSet object unchanged. Here, contains() method helps to provide this information.
Due to the above reason there is no get(Object o) method in HashSet.
Q4 What is the difference between HashSet and TreeSet ?
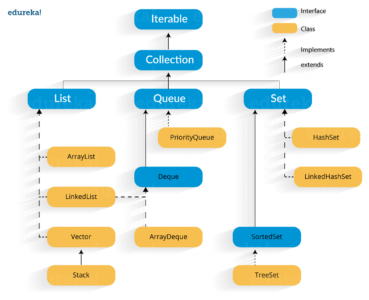
This is one of the most popular java interview questions. Please find the answer here : Difference between HashSet and TreeSet .
Q5 What is and when to use Collections.emptySet() . What is the advantage of having emptySet in Collections class ?
 According to Oracle docs ,Collections.emptySet() returns the empty immutable Set ,not containing null .
According to Oracle docs ,Collections.emptySet() returns the empty immutable Set ,not containing null .Interviewer : Why we call emptySet() method,as we can also create empty Set using constructor ?
Advantages of using emptySet() method over creating object using constructor are :
1. Immutable : You should prefer to use immutable collection against the mutable collections wherever possible . It becomes handy as multiple threads accessing the same instance of object will see the same values.
2. Concise : You do not need to manually type out the generic type of the collection - normally it is inferred from the context of the method call.
3. Efficient : As emptySet() method dont create new objects , so they just reuse the existing empty and immutable object . Although ,practically,this trick is not that handy , and rarely improves the performance
 Q6 What is the default initial capacity and initial load factor of HashSet object?
Q6 What is the default initial capacity and initial load factor of HashSet object?As we already discussed that HashSet internally uses HashMap . So the default initial capacity and initial load factor of HashSet is same as that of HashMap , that is
Default Initial Capacity of HashSet Object : 16
Initial Load Factor of HashSet Object : 0.75
Iteration performance of the HashSet object depends on the above two factors that is initial capacity and load factor :
a. It is very important not to set the initial capacity too high or the load factor too low if iteration performance is important.
Q7 HashMap is not thread Safe so we have ConcurrentHashMap(thread safe).
Why Java do not have ConcurrentHashSet class just like ConcurrentHashMap , as we know HashSet is also not thread safe and internally use HashMap.
Hashset Sample Program Java download free, software 2014
You can answer that there is no need to have ConcurrentHashSet class in Java . The reason is you can produce a ConcurrentHashSet backed by ConcurrentHashMap by using newSetFromMap method.
According to Oracle docs ,method newSetFromMap is defined as :
'Returns a set backed by the specified map. The resulting set displays the same ordering, concurrency, and performance characteristics as the backing map. In essence, this factory method provides a Set implementation corresponding to any Map implementation. There is no need to use this method on a Map implementation that already has a corresponding Set implementation (such as HashMap or TreeMap).'
Set<Object> weakHashSet = Collections.newSetFromMap( new WeakHashMap<Object, Boolean>());
Parameters:
map - the backing map
Java Hashset Add
Returns:
the set backed by the map
Q8 What is HashSet ?What are the properties of HashSet object?
According to Oracle docs ,
HashSet class implements the Set interface, backed by a hash table (actually a HashMap instance). It makes no guarantees as to the iteration order of the set; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time. This class permits the null element.
One line answer : HashSet allows unique elements in unordered manner.
Properties :
1. HashSet ensures uniqueness ,In other words , every object in the HashSet presents only once
2. Unlike LinkedList, HashSet does not store the objects in orderly manner. It is possible that the object which we added first in the HashSet , may appear last in the output .
3. It offers constant time performance for basic operations like add, remove , contains and size assuming the hash function disperses the element properly among the buckets.
4. HashSet implementation is not synchronized.
* If multiple threads access a hash set concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the set, it must be synchronized externally.
*This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the set.
Q9 Why does HashSet implementation in Sun Java use HashMap as its backing?
In order to reduce Duplication of code and made it Memory Efficient ,HashSet implements HashMap as its backing.
On both 32-bit and 64-bit, HashSet is 4x larger than necessary, and HashMap is 2x larger than necessary. HashMap could be implemented with an array with keys and values in it (plus chains for collisions). That means two pointers per entry, or 16 bytes on a 64-bit VM. HashSet also uses 32 bytes per element, but the waste is 4x instead of 2x since it only requires 8 bytes per element.
Q10 What interfaces are implemented by the HashSet Class ? Which is the superclass of HashSet Class?
HashSet Class implements three interfaces that is Serializable ,Cloneable and Set interfaces.
AbstractSet is the superclass of HashSet Class .
Hashset Sample Program Java Download free. software downloads
Please mention in comments in case you have any doubts or queries .